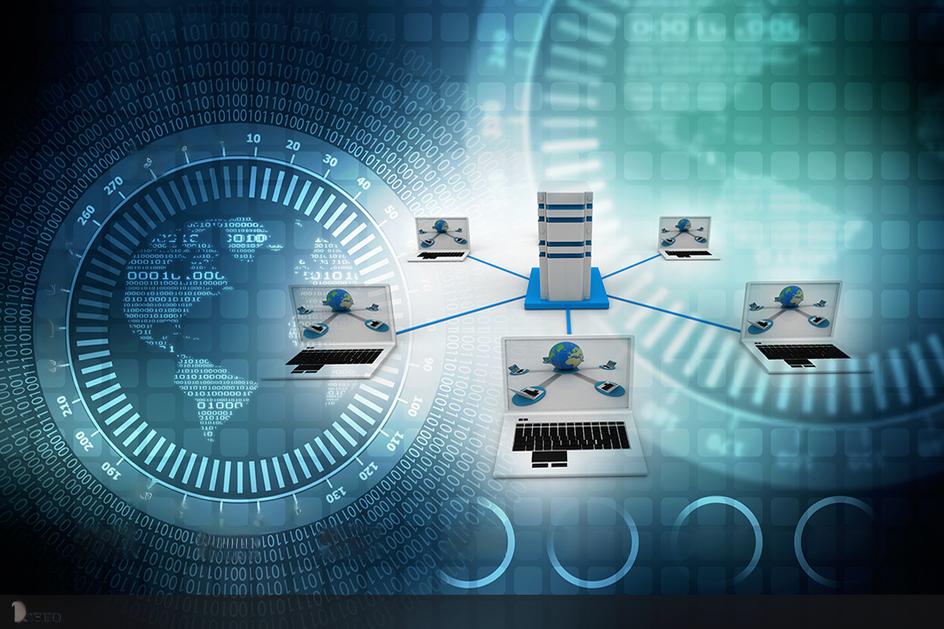
句型结构英语七大句子汇总_句型结构英语七大句子汇总
1.五种句子结构英语例句
2.初中英语句子结构:5种常见句型
3.英语句子的八大基本结构例句
4.英语句子结构及五种基本句型

英语五大基本句型
基本概念:与汉语相似,英语句子是由主语(subject), 谓语动词(verb),宾语(object), 表语(predicative),状语(adverbial),宾语补足语(object complement)等成分组成,按照这些成分的组合方式英语句子可分为五种基本句型。
句型一:主语+不及物动词
不及物动词本身就可以表达完整的意念, 不需要宾语及补语, 但有时可有副词, 介词短语等状语修饰语。
e.g. The rain stopped .
The old man walks in the park .
句型一的扩展:1.主语+不及物动词+状语
e.g. The machine works smoothly. (机器运转正常。)
2.There +不及物动词+主语
e.g. There is some milk in the bottle .
There comes the bus .
3. 主语+不及物动词+ 动词不定式
e.g. They stopped to take a short rest . (他们停下来稍作休息)
特别提醒
动词stop 可用作不及物动词,也可用作及物动词。作不及物动词时, 通常后接动词不定式,表示停下来的目的是做另一件事。作及物动词时,通常后接动名词,表示停止做这件事。
e.g. They stopped taking a rest .
句型二 :主语+系动词+表语
系动词本身不能表达完整的意念没,需要形容词,名词,介词短语等来补充说明主语,也叫主语补语。
e.g. My sister is a nurse .
I feel quite hungry .
The ball is under the desk .
句型三:主语+及物动词+宾语
及物动词本身需要一个动作的接受者(宾语),才可以表达一个完整的意念。
e.g. We are learning English .
Do you know him ?
Your radio needs repairing .
She hopes to see her uncle.
句型四:主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语
有些及物动词需要两个宾语才能表达一个完整意念。
e.g. Her mother bought her a skirt.
Give me the book, please.
特别提醒
A. 在此句型中, 通常是间接宾语(人)在前,直接宾语(物)在后,有时直接宾语和间接宾语可以对调,这时间接宾语前应加上适当的介词。
e.g. Her mother bought a skirt for her .
Give the book to me , please .
直接宾语与间接宾语对调时,间接宾语前加介词to的动词有:
give(给), tell(告诉) , lend(借给) , sell(卖), teach(教) , send(寄给), write(写给), show(出示) , return(还给), bring(带给), pass(递给), lee(留给), offer(提供), hand(交给)
间接宾语前加介词for的动词有:
buy(买), choose(选择), get (弄到), make(做), order(订购), sing (唱歌), do (做), play(演奏)
B. 如果直接宾语为人称代词那么必须把直接宾放在间接宾语前,且间 接宾语前要加上适当的介词。
e.g. I handed it to our teacher .
不能说:I handed our teacher it .
C. 此句型变为被动语态时,可分为两种情况。
e.g. Her mother bought her a skirt .
a. She was bought a skirt by her mother .
b. A skirt was bought for her by her mother.
句型五:主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语
及物动词本身需要一个宾语外, 还需要一个名词,形容词,副词, 动词不定式,分词来补充说明宾语,才能表达一个完整的意念。
e.g. We elected Li Yang our monitor.
The news made us sad.
She saw the thief steal into the shop .
The teacher asked me to answer the question .
I found the man stealing the money .
I found my money stolen .
特别提醒
A. 现在分词为宾语补足语时,宾语与现在分词之间是主动关系;过去分词为宾语补足语时,宾语与过去分词之间是被动关系。
B. 在let(让),make(使得),he(请,让,使得),see(看),hear(听到),watch(观看),feel(感觉到),listen to (倾听),look at (看到),notice(注意到)等动词后的宾语补足语如果为不定式, 则省掉”to”,但变为被动语态时, 则要带”to”.
e.g. We hear her sing next door.
She is heard to sing next door .
C. 此句型变为被动语态时,只有一种情况。
e.g. They saw him steal the old man’s money.
He was seen to steal the old man’s money .
五种句子结构英语例句
下面是我整理的 英语写作 必备句式结构大全, 希望对大家有帮助。
英语写作必备句式结构大全
陈述句中有肯定句与否定句之分。其中可以分为以下五种:
① 主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语,如:I found it impossible to do it. Please keep the classroom clean and tidy.
② 主语+及物动词+宾语,如:I bought a good English Chinese Dictionary yesterday.
③ 主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语,如:Please tell me a story before I go to bed. 这样可加双宾语的 句子 有buy,tell, give, ask, pass, teach.
④ 主语+不及物动词。如:I arrived at six last night.
⑤ 主语+系动词+表语,如:Tom is an American boy. The grass turned green in spring.
在初中常见的句型中有There be?句型,表示存在某种事物,如:There is a map on the wall 其be动词的形式要与其后 面相 近的那个名词相一致。要注意的是这种句型加入助动词后,也要保持be动词,不要换用he,如:There is going to be a meeting tomorrow.
在句子结构中要注意主谓一致的问题,即句子的主语与谓语动词要相呼应。要注意的有如下几点:
① 用and连接两个主语时一般应视为复数,但如一人身兼两职时则要用单数谓语动词形式,如:A singer and dancer is coming to our party. a singer and dancer 既歌唱又可舞的演员。而 a singer and a dancer 则要译为:一位歌唱家和一位舞蹈家。
② 有些以 s 结尾的名词谓语动词要用单数,如: The news is good (news为不可数名词)。
③ 有量词时应按量词的数量计算;如: This pair of glasses is good My glasses are broken.
④ 有些形单却意为复数的名词,如: People are coming here 这样的词还有 Police,如果要讲一个警察时,应讲 a policeman。两个警察为 two policemen。又如 a policewoman, two policewomen
⑤ 所有不定代词 each, either, neither, one, the other, nobody,nothing, anyone, anything, someone, something ?要作为单数如: Someone is waiting for you 在并列句中表示联合关系的连词有:and not only ? but also, neither ? nor, either ? or 如: My sister and my parents are going to the cinema。表示转折关系的并列连词有: but和 yet,如: She is a good student, but she didn't pass the final exam.又如: I think the news is strange, yet it is true 表示选择关系的连词有:or, either ? or,如: Hurry up, or you will be late for school 表示因果关系的并列连词有: for, so 如: They studied very hard, so they all passed the exam
宾语从句
① 在及物动词的后面可以接一个名词来充当宾语,如: I knew the man, 而这时也可以用一个句子来充当宾语,如: I knew that he was a good man 这时宾语从句的连接词有 that, (that 只在从句中起联接作用,不在句中充当语法成分,既不是主语也不是宾语,所以在口语中常常被省略。如: I am sure (that) she has passed the exam
② if, whether 它们在宾语从句中只起连接作用,不起语法作用,当作是否讲。从句中有 or not 结构时,要用 whether, 如: I ask him if (whether) he has had his lunch I asks him whether he has had his lunch or not
③ what 它在宾语从句中除了作连接词外,还要作主语或宾语成份,如: I don't understand what you said (what 作 said 的宾语)。又如: I asked him what made him sick (what 在宾语从句中作主语)。
④ who,它也和what一样,在句中除作连接词外,可以充当句中的成份,如:I know who she is looking for?
⑤ whose 如: I want to know whose book this is?
⑥ which 如: Do you know which book is mine?
在连接词中还有4个常用的连接副词,
① how 它的应用最广,如: how much, how many, how long, how soon, how old ?。如: How much does it cost?
② when 它只是连接时间状语,如: Please tell me when the meeting will begin?
③ where 它连接地点状语,如: Where are you from?
④ why 它要连接的是原因状语从句,如: The teacher asked why Tom didn't come to school.
在考试中常见到的考点是:宾语从句的时态与主句时态的呼应问题。 ①主句谓语动词如果是现在时或将来时,宾语从句的时态可以是任何所需要的时态,如: I know he didn't come. 我知道他没来。 I know he will come tomorrow 我知道他明天来。I know he has gone to London 我知道他已去伦敦了。
②主句中的谓语动词若是过去时,宾语从句也要用过去时态中的某一种。比如:一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时,过去完成时。除了在表达宇宙中的客观真理时,不能用现在时态。如: I wanted to know when he would come The teacher told me the earth moves around the sun
时间状语从句
其连接词有:after, before, when, as, as soon as, until (till),while, since, by 其中较难掌握的有以下几点
① until (till) 直到,在用 until 表达时间状语的句子中,主句中的动词是要十分小心去选择。如动词是持续性动词,它要用肯定句,如: I studied hard until 12 o'clock last night. 如果动词是瞬间截止性动词,则要用否定句,如: He didn't go to bed until his mother came back
② 由 since, for, by, before 来引导的时间状语从句。 since 引导的时间状语是动作的开始时间,如: I he studied English since 1990. 而由 by引导的时间状语通常是动作的结束时间,如: I had learned 25 English songs by the end of last term 而before 则多用于完成时, ago 则多用于一般过去时,如: He had finished his work before twelve yesterday I left my hometown two years ago
③ 在状语从句中用一般现在时或一般过去时表示将来。它们可能是主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时,如: If it rains, they won't go to the park on Sunday 也可以主句是一般过去时,从句用一般过去进行时,如: He said if it rained the next day he would not go to the park
④ 考试中常见的考点有:要学生区别是条件、时间状语从句还是宾语从句,因在宾语从句中该用什么时态用什么时态,如: I want to know if he will come here tomorrow 在宾语从句中的条件状语从句与主句的关系,如: I want to know if it rains he will come here tomorrow
原因状语
① because,应译为"因为"。它表达的因果关系最强,如: He didn't pass the exam because he didn't study hard
② since 应译为"既然",如: Since you were ill yesterday I left some notes on your desk
③ as 应译为"由于",如: As it is too hot we'd better go swimming since 与as 所表达的因果关系远比 because 弱得多。而 for 表达的因果关系最弱。它不能用于句首,如: He studies hard, for he wants to go to college
比较状语从句
同级比较 as ? as,如: This book is as good as that one 要注意的有两点:
① as ? as 中间要用原级而不是比较级。
② 用形容词还是副词,如: Mary writes as carefully as Tom 而其否定句为not as (so) ? as,如: They didn't work so hard as we did, 而不同级比较用比较级加 than, 如: He is younger than I am
要注意的是表示"越来越"这一概念时有两个句型:
① 比较级+and+比较级,如: The days are getting longer and longer The little girl is becoming more and more beautiful
② 定冠词 the +比较级+ the +比较级,如: The harder you study, the more you can learn 方式状语中要注意的是as (连词)与 like (介词)的区别。 as 作为连词其后接从句,如: Please do it as I did it 但后面的句子常作省略,如: Please do it as I 而 like 是介词,其后要接的是宾语,如: Please do it like me
结果和目的状语从句
主要有 so ? that, so that, in order that等几种用法。
① so ? that 用在单数可数名词前,so +形容词+ a +名词+ that,如: She is so beautiful a girl that everyone likes her 或用 such + a +形容词+名词+ that, 如: She is such a beautiful girl that everyone likes her
③ 在不可数名词或可数名词复数前只能用 such,如: It is such good weather we want to go for a picnic 又如: They are such good players that they should win the game.
④ 在much, many, few, little 之前只能用so,如: I he so little money that I can't buy it
⑤ so ? that 之间只有形容词时,则不能用 such,如: It is so good that I want to buy
⑥ so tha
以上是一些比较基础的英语句式,它有助你写 英语 作文 ,希望你的英语成绩能有所提高。
初中英语句子结构:5种常见句型
五种句子结构英语例句如下:
1、主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语的句型。在这类句型中,谓语是可以带宾语的及物动词。比如:Helike learningEnglish.他喜欢学习英语。 This machine needsrepairing.这台机器需要修理。Theyhelefttheclassroom.他们已经离开教室了。
2、主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语的句型。在这类句型中,谓语动词是可以带两个宾语的及物动词。比如:Her father bought her fresh fruit.爸爸给她带新鲜的水果。Givemeacup teaplease请给我一杯茶。
注意在这类句型中,有时候我们会把直接宾语和间接宾语对调,这时间接宾语前面要加上一个介词。比如Her father bought a toyforher爸爸给她带了一个玩具 Give scup coffee to meplease.请给我一杯咖啡。
3、主语+谓语动词+宾语+补语的包型。 在 这类句型中,谓语动词是及物动词。这类及物动词除了需要一个宾语以外,换需要一个名词、动词不定式、形容词、副词或者分词来对宾语进行补充说明,才能表达完整。比如:Mother asked me to clean thebedroom.妈妈让我去打扫卧室,The news made ucited.这个消息让我们振奋。
英语句子的八大基本结构例句
句子 是 文章 的组成部分,只有组成了句子才有真正的意义。在英语 文章阅读 中,语法归根结底是为我们读懂文章而服务的,只要能够掌握基本的语法规律,无障碍的读懂复杂的句子,语法的任务就圆满的完成了。下面我就介绍5中初中英语句子机构常见句型:
一、Subject (主语) + Verb (谓语)
这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词,所谓不及物动词,就是这种动词后不可以直接接宾语。常见的动词如:work, sing, swim, fish, jump, arrive, come, die, disear, cry, hen等。如:
1) Li Ming works very hard.李明学习很努力。
2) The accident hened yesterday afternoon.事故是昨天下午发生的。
3)Spring is coming.
4) We he lived in the city for ten years.
二、Subject (主语) + Link. V(系动词) + Predicate(表语)
这种句型主要用来表示主语的特点、身份等。其系动词一般可分为下列两类:
(1)表示状态。这样的词有:be, look, seem, smell, taste, sound, keep等。如:
1) This kind of food tastes delicious.这种食物吃起来很可口。
2) He looked worried just now.刚才他看上去有些焦急。
(2)表示变化。这类系动词有:become, turn, get, grow, go等。如:
1) Spring comes. It is getting warmer and warmer.春天到了,天气变得越来越暖和。
2) The tree has grown much taller than before.这棵树比以前长得高多了。
三、Subject(主语) + Verb (谓语) + Object (宾语)
这种句型中的动词一般为及物动词, 所谓及物动词,就是这种动词后可以直接接宾语,其宾语通常由名词、代词、动词不定式、动名词或从句等来充当。例:
1) He took his bag and left.(名词) 他拿着书包离开了。
2) Li Lei always helps me when I he difficulties. (代词)当我遇到困难时,李雷总能给我帮助。
3) She plans to trel in the coming May Day.(不定式)她打算在即将到来的“五一”外出旅游。
4) I don?t know what I should do next. (从句)我不知道下一步该干什么。
注意:英语中的许多动词既是及物动词,又是不及物动词。
四、Subject(主语)+Verb(谓语)+ Indirect object(间接宾语)+Direct object (直接宾语)
这种句型中,直接宾语为主要宾语,表示动作是对谁做的或为谁做的,在句中不可或缺,常常由表示“物”的名词来充当;间接宾语也被称之为第二宾语,去掉之后,对整个句子的影响不大,多由指“人”的名词或代词承担。引导这类双宾语的常见动词有:buy, pass, lend, give, tell, teach, show, bring, send等。如:
1) Her father bought her a dictionary as a birthday present.她爸爸给她买了一本词典作为生日礼物。
2)The old man always tells the children stories about the heroes in the Long March.
老人经常给孩子们讲述长征途中那些英雄的 故事 。 上述句子还可以表达为:
1)Her father bought a dictionary for her as a birthday present.
2)The old man always tells stories about the heroes to the children in the Long March.
五、Subject(主语)+Verb (动词)+Object (宾语)+Complement(补语)
这种句型中的“宾语 + 补语”统称为“复合宾语”。宾语补足语的主要作用或者是补充、说明宾语的特点、身份等;或者表示让宾语去完成的动作等。担任补语的常常是名词、形容词、副词、介词 短语 、分词、动词不定式等。如:
1)You should keep the room clean and tidy. 你应该让屋子保持干净整洁。(形容词)
2) We made him our monitor.(名词)我们选他当班长。
3) His father told him not to play in the street.(不定式)他父亲告诉他不要在街上玩。
4)My father likes to watch the boys playing basketball.(现在分词)
5) Yesterday I had a picture taken with two Americans.(过去分词)
● 常见的动词有: tell, ask, advise, help, want, would like, order, force, allow等。
● 注意:动词he, make, let, see, hear, notice, feel, watch等后面所接的动词不定式作宾补时,不带to。如:
1) The boss made him do the work all day.老板让他整天做那项工作。
2) I heard her sing in the next room all the time last night.昨天晚上我听见她在隔壁唱了一个晚上。
英语句子结构及五种基本句型
英语句子的八大基本结构:
1.第一种句型:主-谓(SV)
这种句型里的谓语一般是不及物动词,后面可以跟状语。
例Everybody went.
2.第二种句型:主-系-表(LSP)
前面第一句分析时有分享过这种句型里的系动词的用法,系动词在形式上是一种谓语动词,而表语实际是主语的补语,所以一般也将这种结构叫做“主-谓-补”(SVC)
例The lees are yellow.
3.第三种句型:主-谓-宾(SVO)
在这种句型里,谓语一般是及物动词,后面要跟宾语,这里的宾语一般都是直接宾语。宾语可以由名词、代语、数词、动名词、分词、不定式或从句来充当。
例The house caught fire.
4.第四种句型:主-谓-宾(直接)-宾(间接)(SVOO)
这个句子里涉及到两个宾语,所以谓语动词必须是可有双宾语的及物动词,也就是传说中的与格动词。
何谓与格动词?有解释说“它是直接宾语与间接宾语的不完全及物动词,有把某物从一个人转移给另一个人的意思”。直白一点就是谁把什么东西给了谁等类似的意思。直接宾语常指物,间接宾语常指人,相关的动词有give, provide, buy, write, ask等。
例I ge my son the book. 我把书给了我儿子。give就是与格动词,后跟两个宾语my son, the book.
5.第五个句型:主-谓-宾-宾补(SVOC)
在该句型里,宾语补足语与宾语一起组合构成复合宾语,要求谓语必须是可以带复合宾语的及物动词,如find, hold, let, heard等。
例I found the project difficult. difficult就是宾语project的补足语.
6.There be句型
There+be+主语+状语
这个句型其实属于倒装的一种,主语后置,there作为引导词,无实际意义。
例如:There are many children in the park.
7.主语+谓语+状语
这个句型是在主谓结构后通过状语对语义进行修饰补充,充当状语的一般是副词、介词短语等。
例如:She arrives early.
8.主语+谓语+宾语+状语
这个句型是在主谓宾结构后面通过状语进行修饰补充。
例如:I drive my car everyday.
回答如下:
分析英语句子时:你只需记住一个口诀。一个中心+两个要点
一个中心:动词。一个句子里面必须要有动词。
两个要点:主语+谓语。谓语是动词,主语表示动作的执行者或接受者。
句子的核心是主谓结构。即n个主语+1个谓语?或者?1个主语+n个谓语,就可以组成简单句。
一:S+V (主+谓)此句型的句子有一个共同特点,即句子的谓语动词都能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做不及物动词,后面可以跟副词、介词短语、状语从句等。
So?I?do, master.?
Little Robin?chirped?and?sang.
二:S+V+P (主+系+表)此句型的句子有一个共同的特点:句子谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语身份或状态的表语构成复合谓语,才能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做连系动词。系动词分两类:be, look, keep, seem等属一类,表示情况;get, grow, become, turn等属另一类,表示变化。
I'm?always?alone.?
The storms?grow?stronger.?
He?was?so?small.?
三:S+V+O (主+谓+宾)此型句子的共同特点是:谓语动词都具有实义,都是主语产生的动作,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语,即动作的承受者,才能使意思完整。这类动词叫做及物动词。宾语位于及物动词之后,一般同主语构成一样,不同的是构成宾语的代词必须是‘代词宾格’,如:me,him,them等
Who │knows │the answer? 谁知道答案?
She │smiled │her thanks. 她微笑表示感谢。
He │has refused │to help them. 他拒绝帮他们。
He │enjoys │reading. 他喜欢看书。
四:S+V+IO+DO(主+谓+间宾+直宾)有些及物动词可以有两个宾语,如:give给,pass递,bring带,show显示。这两个宾语通常一个指人,为间接宾语;一个指物,为直接宾语。间接宾语一般位于直接宾语之前。 一般的顺序为:动词 + 间接宾语 + 直接宾语。如:Give me a cup of tea,please.
She │ordered │herself │a new dress.?
She │cooked │her husband │a delicious meal.?
He │brought │you │a dictionary.?
五:S+V+DO+OC (主+谓+宾+宾补)
此句型的句子的共同特点是:动词虽然是及物动词,但是只跟一个宾语还不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个补充成分来补足宾语,才能使意思完整。宾语补足语:位于宾语之后对宾语作出说明的成分。宾语与其补足语有逻辑上的主谓关系,它们一起构成复合宾语。
He'll sit in a barn, and?keep?himself?warm.?
Three?straws?on a staff would?make?a?baby?cry and laugh.?
I?had a little boy, and?called?him?Blue Bell.
声明:本站所有文章资源内容,如无特殊说明或标注,均为采集网络资源。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。