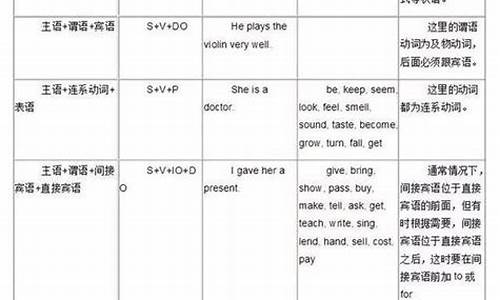
英语句子组成形式_组成英语句子的基本结构
1.帮忙说说英语语法中的句子的构成,各个部分都用什么词
2.英语,改为简单句
3.英语的句子类型有哪几种?
4.英语句子成分怎样判断一个词语在英语句子的成分,
5.句子成分
6.英语的句子形式详解
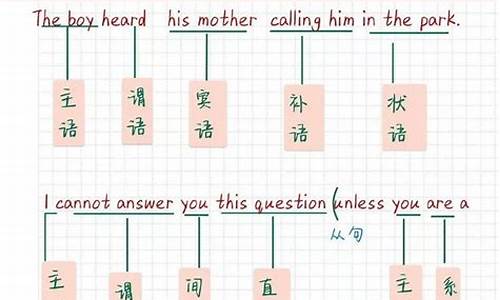
总体而言,英语的句子成分有主语,谓语,宾语,定语,状语,主语补语(常指表语),宾语补语,形容词补语,同位语,独立成分这十类组成,每种成分的常见表现形式最多不超过三类:单词,短语,从句。比方说,以主语为例,您需要再进一步搞清楚哪些单词或短语可以充当该成分,从句作主语有什么注意事项(如作主语的句子是陈述句、一般疑问句、特殊疑问句时各有什么要求及注意须知等等),如此这般将每个成分过上一遍,保证您的语法底子坚如磐石!
主语有两种定义(请务必注意句子成分的定义与句子结构是密不可分的!!!)
1.在“主语+谓语”结构中,主语是陈述/被陈述的对象或说明/被说明的事物。
1)主语+ 系动词+ 表语 :He is a fanciful writer(他是一位富有想象力的作家。)
2).主语+ 半系动词+表语:
She looks lovely in white.(她穿白色衣服看上去很漂亮。)
His face went cool again.(他的面孔又变冷漠了。)
she remained serene and in control.( 她依旧泰然自若。)
Our vision ears limited.(看来我们的目光短浅。)
注:请特别注意以上四句的谓语动词,它们在这里代表着四组不同类别的半系动词
3)主语+不及物谓语动词/ 不及物动词短语:
The breeze has died away.( 微风渐渐止住了.)
2.在“主语+谓语+宾语”结构里,主语是动作的发出者。
能够作主语的一般有:名词、代词、数词、动名词、名词化的形容词即:the+形容词表示每一类的人或物,如:the rich(富人),the poor(穷人)等),此外还有动词不定式、动名词短语,名词短语,形容词短语,代词短语和从句(即主语从句)。
谓语同样也是两类定义:
1)在“主语+系动词+表语”结构中,谓语=系动词+表语,在 “主语+不及物谓语动词/不及物动词短语”中,谓语就是该不及物动词或不及物动词短语。
2)在“主语+谓语+宾语”结构中,谓语是主语所发出的动作。此时谓语由动词来担任。(详情参阅链接提示中内容)
宾语总体分为动宾和介词宾语两大类,动词宾语是仅指“主语+谓语+宾语+......”类结构而言,宾语是主语所发出的动作的承受者,介词宾语则是指放在介词后面单词、短语或从句(详情请参看英语语法书)宾语可由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式、动名词、宾语从句等来担任。
定语是用来修饰名词或代词的修饰限定成分,放在被修饰词的前面或后面。(一般称为“修饰、限定名词或者代词的成分”。
定语有两类,位于被修饰词之前的单个词或者合成词称作前置定语;位于被修辞之后的单词、短语或从句称作后置定语。前置定语可以由名词,形容词和起形容词作用的词(如数词、现在分词、过去分词)来担任;后置定语则由形容词、介词短语、现在分词短语、过去分词短语和从句来担任。
前置定语见以下例句:
There is a a baby girl in the cradle. (摇篮里有一个女婴)baby就是名词作前置定语。
I am waiting for your reply. (我在等你答复) your就是形容词性物主代词作前置定语。
He is a business- is –business man.(他是一个公事公办的人) business- is –business 就是合成词作前置定语。
后置定语分为三类,详情见下:
单词:
1)以a开头的形容词: a world anew 一个崭新的世界(其中,anew就是后置定语,用来修饰限定world 。)
2)修饰限定“复合不定代词”的形容词:I he something important to tell you.我有些重要的事情要对你说。(其中,important 就是后置定语用来修饰something.)
短语:
1)He had the ability to push aside all difficulties 他有能力排除一切困难。
(句中,to push aside all difficulties 就是动词不定式作后置定语,修饰ability.)
2)The girl in red is his sister. 穿红衣服的那个女孩是他妹妹。
(句中介词短语in red 就是The girl 的后置定语)
3)I hopped into a taxi standing at the door. 我跳进一辆停在旅馆门口的出租车。
(句中,standing at the door就是现在分词短语作a taxi 的后置定语)
4)He is a man rude but henpecked.他是一个粗暴而惧内的男人。(形容词短语作后置定语)
从句:
1)He lives in the house which is opposite ours. 他住在我们对面的那栋房子里。(句中,从句which is opposite ours就是the house 的后置定语)
2)This is a pretty flower, whose name I don't know. 这是一种很美的花,我不知道它叫什么名字.
(句中,whose name I don't know就是a pretty flower的后置定语)
补语有三大类:
主语补足语:一般多体现为表语形式,表语即是主语补足语的最常见的一类。
宾语补足语(放在宾语后面补充说明宾语的成分)
形容词补足语:放在形容词后面,用来补充说明该形容词的内容,原因等的成分。例如:
I am glad to see you again.(我很高兴再次见到你。)本句中的to see you again就是动词不定式作形容词glad的补语,补充说明高兴的原因,再如:
Mike is confident that he will arrive in time. (迈克相信他会及时到达。 )句中的confident 就是形容词,其后的 that he will arrive in time就是形容词补语从句。
状语包含的内容很复杂:用以说明地点、时间、原因、目的、结果、条件、方向、程度、让步、方式和伴随、比例、比较等十余种概念的成分称作状语,具体表现形式为“单词、短语、从句”三类,状语一般由副词、介词短语、分词和分词短语、不定式或相当于副词的词或短语以及从句来担当。其位置一般放在句末,但也可放在句首或句中。 (详情请参看英语语法书“状语章节”,此处不多赘叙。
以上是句子中重要成分的介绍,余者还需参看语法书)
至于您末尾的一问,可以100%的肯定答复您:You are my best friend不是主谓宾结构,而是“主语+系动词+表语”结构,You是主语,are是系动词,my best friend是表语,其中,my 和best都是friend的前置定语, are my best friend是“系动词+表语”充当合成谓语,所以整个句子又可以说是属于一种“主语+谓语”结构
帮忙说说英语语法中的句子的构成,各个部分都用什么词
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
句型转换题是中考常见题型,它主要用来考查大家对句子结构的构成、变化的掌握及在行文中的运用等,类型繁多。现以近两年中考题为例,分类介绍如下:
[第一类] 改成否定句
英语中有关否定的结构各不相同,除动词部分构成的否定外,还有名词、代词的否定、部分否定、否定转移、以及一些表示否定意义的短语或句型等。
一、含有连系动词、情态动词等助动词的句子改为否定句时,在连系动词、情态动词等的后面加not就行了。如:(划线部分为正确答案,下同。)
1. He was late for school yesterday. (2005黑龙江省泰州市)
He wasn’t late for school yesterday.
2. The students of No.2 Middle School he gone for a picnic already. (2004新疆)
The students of No.2 Middle School hen’t gone for a picnic yet.
二、祈使句变否定句一般在其前加don’t。如:
3. Open the window. (2005江苏省)
Don’t open the window.
三、实义动词的否定式是在实义动词前加don’t, doesn’t, didn’t等。如:
4. She does the housework every day. (2005黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
She doesn’t do the housework every day.
5. He returned the book to the library this morning. (2004重庆市)
He didn’t return the book to the library this morning.
注意:变否定句时须注意某些词语的变化,如some改为any, something改为anything, already改为yet, both改为neither, all改为none等。又如:
6. Both of them are my best friends. (2004甘肃省兰州市)
Neither of them is my best friend.
[第二类] 改为疑问句
可分为一般疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
一、变一般疑问句时,含有连系动词、情态动词的句子,只需将它们移至句首,第一个字母变为大写,句尾改为问号即可。含有实义动词的句子,在实义动词前加do, does, did等。变化过程中也要注意某些词语和人称的变化。如:
7. There’s something to eat in the cupboard.(2005贵州省贵阳市)
Is there anything to eat in the cupboard?
8. Kate does morning exercises every day. (2004山东省济南市)
Does Kate do morning exercises every day?
9. Ann returned the book to the library yesterday. (2005四川省成都市)
Did Ann return the book to the library yesterday?
二、变选择疑问句时,如果该句是一般疑问句,则在后面直接加“or+另一选择部分”就行了;若是陈述句,则要先变成一般疑问句。如:
10. John is an American. (用a Canadian改为选择疑问句)(2004新疆)
Is John an American or a Canadian?
三、变反意疑问句时,要注意“前肯后否”和“前否后肯”,还要注意一些特殊形式的反意疑问句。如:
11. She has hardly had anything this morning, has she?(2005山东省泰安市)
12. You will meet your friends at the railway station, won’t you?(2004重庆)
13. She had nothing for breakfast, did she?(2005青海)
14. There was no time for the twins to go shopping, was there?(2004黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
英语,改为简单句
记住十二个字研究透即可:三大句型六大成分十大词类。
英语句子千变万化,其实就三个基本句型。
主系表
主谓
谓主(主谓结构的特殊形式)即there 加不及物动词加主语
主谓宾
主谓间宾直宾
主谓宾宾补
句子成分 有主语谓语宾语表语定语状语宾补同位语。
词类有 名词代词数词动词形容词副词冠词介词连词感叹词
主语和宾语由名词或相当于名词的词充当。谓语由动词充当。
表语由形容词介词短语名词代词数词方位副词或相当于名词或形容词的词充当。
定语由形容词介词短语或相当于形容词的词充当。
状语由副词介词短语或相当于副词的词充当,
充当宾补的词类与表语类似。
英语的句子类型有哪几种?
Doctors study for at least five years after finishing school.
简单句
根据语法形式,即句子的结构,英语的句子可分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
简单句的基本形式是由一个主语加一个谓语构成。其它各种句子形式都是由此句型发展而来,如五大基本句型:
1.主语+谓语,这种句型简称为主谓结构,其谓语一般都是不及物动词,例:
Things change.事物是变化的。
Nobody went.没有人去。
--Did you go by sea?你们走的是海路吗?
--NO,we flew.不,我们是飞去。
2.主语+连系动词+表语,这种句型称为主系表结构,其实连系动词在形式上也是一种谓语动词,但实质上表语成了谓语,例:
Mr. Turner is an artist.特纳先生是位画家。
The milk turned sour.牛奶变酸了。
She became a lawyer.她当了律师。
3.主语+谓语+宾语,这种句型可称为主谓宾结构,它的谓语一般多是及物动词,例:
We never beat children.我们从来不打孩子。
My sister will fix everything.我姐姐会料理一切。
4.主语+谓语+宾语+宾语,这种句型可称为主谓宾宾结构,其谓语应是可有双宾语的及物动词,两个宾语一个是间接宾语,一个是直接宾语,例:
He ge the book to his sister.他把这本书给了他的妹妹。
I'll write you a long letter.我将写给你一封长信。
5.主语+谓语+宾语+宾补,这种句型可简称为主谓宾补结构,其补语是宾语补语,与宾语一起即构成复合宾语,例:
I found the book easy.我发现这本书不难。(形容词easy作补语)
I'll let him go.我将让他去。(不定式go用作补语)
注意:有时两个或更多的并列主语拥有一个共同的谓语,甚至并列有两个主语和两个谓语,这样的句子仍然是简单句,例:
China and other countries in the east Asia are developing rapidly.中国和东亚其它国家正在迅速地发展。(China and other countries并列主语)
Mr. Wang and I often work together and help each other.王先生和我常在一起工作互相帮助。
多做题就会了。
英语句子成分怎样判断一个词语在英语句子的成分,
一般有简单句、复合句、并列句。
复合句:也就是简单句的某个成分变成丛句了。
是由主句+从句构成,它是英语中比较复杂的句子结构。一般来说,英语中一个句子只能有一个谓语,如果出现两个谓语动词,那么其中一个谓语动词只能以从句的形式或并列句或非谓语动词的形式出现。所谓从句是指从属于主句的句子,由从属连词连接。从句的种类有很多,但根据其性质和作用可以分为:名词性从句,形容词性从句(即定语从句),副词性从句(即状语从句)三大类
并列句
:也就是几个简单句或复合句搞在一起
由连接词或
"
"把两个以上(含两个)的简单句连在一起的句子叫做并列句。在并列句中,各个简单句意思完整,不受其他简单句的影响。
These
flowers
are
white
and
those
flowers
are
red。
这些花是白色的而那些花是红色的。
1.
简单句的五种形式:
(1)主语+谓语(不及物动词);
(2)主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语;
(3)主语+谓语+宾语+补语;
(4)主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语;
(5)主语+系动词+表语。
两类系动词:①be动词;
②一些实义动词用作系动词:feel,
taste,
smell等;
2.
并列句:一个句子当中包含两个或更多互不相依存的主谓结构,中间用一些连接词连接起来的句子。
并列句不能只用逗号隔开,而要用连接词连接。
简单句和并列句是复合句的基础。
句子成分
句子的组成部分,包括主语、谓语、宾语、定语、补语、状语、表语七种
主语是句子叙述的主体,可由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式、动名词和主语从句等来承担.
谓语说明主语所发出的动作或具有的特征和状态.谓语由动词来承担.
宾语是动作的对象或承受者,常位于及物动词或介词后面.宾语可由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式、动名词、宾语从句等来担任.
主语和谓语是英语句子的两大成分,除少数句子(如祈使句和感叹句等)外,一句话必须同时具有主语和谓语所表达的意思才能完整.主语是针对谓语而言的,是一句话的主题,谓语用来说明主语的情况,为主语提供信息.例如:They are working.主语是they(他们),那麽他们在做什麽呢?看来没有谓语are working 是不行的.在正常情况下,英语的主语和谓语的位置与汉语一致,也就是说主语在前,谓语紧跟其后.那麽,哪些词语可以做主语,谓语,何时主谓倒置,主语与谓语的一致情况如何,我将一一讲述.
一、哪些词可以充当主语
1,名词
例如: A mooncake is a delicious, round cake.
The first truck is carrying a few baskets.
The temperature will stay above zero.
The doctor looked over Mrs. Brown very carefully.
China does not want to copy the USA’s example.
2,代词
例如: It’s a young forest.
I don’t know if it will grow.
That’s a bit expensive.
You’d better buy a new pair.
I’m afraid we hen’t got any black shoes.
3,数词
例如:One and two is three.
One is not enough for me. I want one more.
One of them is English.
Suddenly one of the bags fell off the truck.
Two will be enough.
4,不定式 (常以 It’s adj. to do sth. 形式出现)
例如: To give is better than to receive =Its better to give.
I found it difficult to get to sleep.
It’s glad to see you again.
It was difficult to see.
But it’s good to swim in summer.
5,IT 作主语,有如下情况:
1)指代刚刚提到的事物:What’s this ? It’s a bus. (指代what)
2)指代一个你不知道或判断不清性别的人:Who’s knocking the door? It’s me. (指代 who)
Who’s the baby in the picture? It’s my sister. (指代 who)
3) 表示时间,天气,距离:
What’s the time? It’s eight o’clock. (时间)
What’s it going to be tomorrow? It’s going to be rainy.(天气)
How far is it? It’s about one kilometre away. (距离)
6. THERE 引起的There be 句型中,be 作谓语,主语位居其后.如:
There are many different kinds of mooncakes.
There will be a strong wind.
二、谓语
谓语有动词构成,依据其在句中繁简程度可把谓语分为简单谓语和复合谓语两类.不论何种时态,语态,语气,凡由一个动词(或动词词组)构成的谓语都是简单谓语.例如:
I like walking.(一般现在时主动语态)
I made your birthday cake last night. (一般过去时主动语态)
It is used by trellers and business people all over the world. (一般现在时被动语态)
复合谓语也可分为两种情况:
第一种是由情态动词,助动词+不带to的动词不定式构成的复合谓语:
What does this word mean?
I won’t do it again.
I’ll go and move away the bag of rice with Lin Tao.
You’d better catch a bus.
第二种是由连系动词+表语构成的复合谓语.例如:
You look the same.
We are all here.
The weather gets wamer, and the days get longer.
Keep quite and listen to me.
He looked worried.
We he to be up early in the moming.
Is Bill in?
School Is over. Let’s go home.
My pen is in my bag.
I feel terrible.
I* fell tried all the time.
He seemed rather tired last night.
连系动词和表语在意思上紧密联系,不宜分割;有关动词的种类这方面知识在课本中已有介绍,此处不多说了.
三、主语与谓语的一致
英语句子的主语和谓语的一致性,是英汉两种语言的区别之一.具体说来有如下特征:
1, 谓语动词在人称和数上应与主语保持一致.如:
Now the teacher es into the classroom.
本句属一般现在时,主语the teacher 为第三人称单数,因而谓语动词e 应加s.
One morming she was working at her desk in the library wher a boy came in. 本句属主从复合句,主句用过去进行时,从句为一般过去时;主句中主语she为第三人称单数,所以谓语为 was working.
1) 主语含有 and 时,如表示一个单一的概念,谓语动词常用单数(特别是当and 连接的是两个不可数名词时),否则用复数.如:
One and three is four. And 前后均为数字,表示同一个概念,谓语动词应用is.
Tea and milk is my fourite drink. 本题中tea and milk 指一种饮料,故谓语用is.
Tom and Li Lei are my best friends. Tom 和 Li lei 是完全不同的两个人,有不同的特征,因而谓语是are.
2) 主语为动词不定式时,其谓语常用单数形式.如:
To give is better than to receive.
It was difficult to see.
It’s best to wear cool clothes.
同样,动名词作主语,谓语动词也为单数.初中阶段只学了一句:
It (playing) is much better than hing classes.
3) 不可数名词作主语,谓语动词视为单数.如:
The best time to e to China is autumn.
The weather in England never gets too hot.
4) 在姓的复数前加the 表示一家人,谓语动词为复数.如:
What time do the Reads he breakfast? 主语是the Reads, 表示里得一家人,谓语动词用do….he.
5) 表示时间的复数名词作主语,常作整体看待,其谓语动词为单数形式.如:
Two months is quite a long time.
6) “几加几等于几”的算式中,谓语动词常为单数.如:
Twenty and forty is sixty.
主 谓
7) 某些表示学科的名词作主语,无论其结尾是什麽,谓语动词都视为单数.如:
Maths is my fourite subject.
主 谓
8) each 以及由some,any,no,every 构成的复合代词作主语,谓语动词为单数.如:
There’s something wrong with my ears!
谓 主
Everyone is going into class.
主 谓
9) what,who which 等词做主语,谓语动词形式视意思而定.如:
What is this?(this 为单数,用is)
What are these? (these 为复数,用are )
Which is your friend? 哪一个人是你的朋友?
Which are your friends? 哪些人是你的朋友?
10) None 作主语,其谓语可以是单数,也可以是复数,此项目并非初中阶段重点,故此不谈.
11) People,Chinese, Japanese 作主语,谓语动词为复数.如:
There are four people in my family.
谓 主
The chinese people are very friendly.
12) population 作主语,指“人口”时,谓语为单数;其前有表示数量的修饰语时,谓语为复数;课本第三册只要求掌握作“人口”讲时谓语的情况:
What’s the population of Germany?
谓 主
What was the population of the world in 1950?
谓 主
Half of the population of China are women.
修饰语 主 谓
2, 由 either …or 或neither …nor 连接的两个并列成分作主语,其谓语动词形式与后一个主语保持一致.如:Either Lily or Lucy is going to e.(Lily和Lucy 谁去都行.后一个主语Lucy 为第三人称单数,谓语用is going to e.)
Either I or he does well in English. 我和他的英语都不错.
Neither I nor she likes swimming. 我和她都不喜欢游泳.
由these 和here 引出的含有不只一个主语的句子,其谓语动词形式由最靠近谓语的主语形式决定.如:
These is a pen, two rulers and three books on the desk.
Here are some cups,a glass and some pears on
句子的成分:
构成句子的基本成分叫做句子成分.句子成分可分为主语,谓语,宾语,表语,定语,状语,同位语.它们可以由单词来担任,也可以由词组,以及句子来担任.
主语
主语是一个句子中所要表达,描述的人或物,是句子的主体.
I work here.
我在这儿工作.
She is a new teacher.
她是一个新教师.
主语可以由名词,代词,数词,动词不定式,动名词,名词化形容词,分词,从句,短语等来担任.
The book is on the desk.
书在桌子上.
I get an idea.
我有一个主意.
Two and two are four.
二加二等于四.
When to be ginisnotknownyet.
什么时间开始还不知道.
What I know is important.
我所知道的很重要.
谓语谓语是用来说明主语做了什么动作或处在什么状态.谓语可以由动词来担任,一般放在主语的后面.
We don't know him very well.
我们不太了解他.
She speaks English fluently.
她英语讲得很流利.
表语表语是用来说明主语的性质,身份,特征和状态.表语须和连系动词一起构成句子的复合谓语.表语一般放在系动词之后.表语可以由名词,形容词或起名词和形容词作用的词和短语担任.
These desks are yellow.
这些桌子是**的.
I am all right.
我没事.
We are hy now.
我们现在很幸福.
It's over.
时间到了.
She is ten.
她十岁了.
My work is teaching English,
我的工作是教英语.
The dictionary is in the bag.
词典在书包里边.
My question is how you knew him.
我的问题是你如何认识他的.
宾语
宾语是谓语动作所涉及的对象,它是动作的承受者,宾语可以由名词或起名词作用的成分担任,宾语一般放在谓语动词后面.
I saw a cat in the tree.
我看见树上有一只猫.
I want to go shopping.
我想去买东西.
He said he could be here.
他说他会来的.
We think you are right.
我们认为你是对的.
有些及物动词可以有两个宾语,其中一个宾语多指人,另一个宾语指物,指人的宾语叫做间接宾语,指物的宾语叫做直接宾语,可以带两个宾语的动词有 bring,give,show,send,pass,tell等.间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面,如果强调直接宾语可把直接宾语放在间接宾语的前面, 但间接宾语前须加"to".
My father bought me a book.
我父亲给我买了一本书.
Give the rubber to me.
把橡皮给我.
Please give the letter to XiaoLi.
请把这封信给小李.
有些及物动词除跟一个宾语外,还需要加上宾语补足语,否则意思不完整,它们一起构成复合宾语,复合宾语中宾语和后面的宾语补足语有一种逻辑上的主谓关系,这也是判断是两个宾语还是复合宾语的依据,宾语可以由名词或起名词作用的词担任.
We all call him LaoWang.
我们都叫他老王.
Please color it red.
请给它涂上红颜色.
We found the little girl in the hill.
我们在山上找到了小女孩.
定语用于描述名词,代词,短语或从句的性质,特征范围等情况的词叫做定语,定语可以由名词,形容词和起名词和形容词作用的词,短语担任.如果定语是单个词,定语放在被修饰词的前面,如果是词组,定语放在被修饰词的后面.
That is a beautiful flower.
那是一朵漂亮的花.
The TV set made in that factory is very good.
那个工厂生产的电视机很好.
This is my book,not your book.
这是我的书,不是你的书.
There are more than twenty trees in our
school.
我们学校里有二十多棵树.
I he a lot of things to do.
我有好多要做的事情.
Our country is a developing country.
我们的国家是一个发展中的国家.
状语:说明事物发生的时间,地点,原因,目的,结果方式,条件或伴随情况,程度等情况的词叫状语.状语可以由副词,短语以及从句来担任.
同位语: 当两个指同一事物的句子成分放在同等位置时,一个句子成分可被用来说明或解释另一个句子成分,前者就叫做后者的同位语(ositive).这两个句子成分多由名词(代词)担任,同位语通常皆放在其说明的名词(代词)之后.
英语的句子形式详解
下面是作文网写作技巧栏目为您准备的一篇《句子成分》,帮助您学习英语句子成分分析。
英语语法?英语句子成分分析
句子是按照一定的语法规律组成的,表达一个完整的意义。一个句子一般由两部分构成,即主语部分和谓语部分,这两部分也叫做句子的主要成分。句子的次要成分包括宾语,定语,状语,表语等。句子成分是句子中起一定功用的组成部分。
1)主语:是一句的主体,是全句述说的对象,常用名词,数词或代词担任,一般放于句首。如:
Students study. (学生学习。)
We are friends.(我们是朋友)
这两句话中单词students是个名词,we是代词,它们在句中做主语。
2)谓语:是对主语加以陈述,表示主语的行为或状态,常用动词或者动词词组担任,放在主语的后面。如:
Students study. (学生学习。)
We are friends. (我们是朋友)
这两句话中单词study和are都是动词,study叫做实意动词,are叫做be动词,它们在句中作谓语。
3)宾语:表示行为的对象,常由名词或者代词担任。放在及物动词或者介词之后。如:
They are teachers. ( 他们是老师。)
I play with him. (我和他一起玩。)
这两句话中单词teachers是名词,单词him是带词,它们在句中作宾语。
4)定语:是用来说明或者限制名词的成分,常用形容词或者相当于形容词的短语或从句担任。形容词放在名词之前,相当于形容词的短语或从句放在名词的后面。如:
This is a red sun.(这是个红太阳.)
He is a tall boy.(他是个高个子男孩。)
这两句话中单词red和 tall都是形容词,它们作定语。
5)状语是用来说明动词,形容词,副词或整个句子的成分。常由副词担任。修饰动词时可以放在动词之前,也可以放在动词之后;修饰形容词或副词时放在它们之前。如:
The students study hard. (这些学生学习努力。)
I often write to him. (我常给他写信。)
The bag is too hey. (这个书包太重了。)
这三句话中单词hard 和often修饰的都是动词,第三句话中单词too修饰的是形容词,它们都作状语。
6)表语:用来说明主语的性质或状态。一般由名词或者形容词担任。如:This table is long. (这个桌子是长的。)
通常情况下,主语和宾语前的成分是定语,谓语前的成分是状语,时间词作状语放在句子后面。句子的成分分布如下:
(定语) 主语 (状语) 谓语 (定语) 宾语 (状语)
如:(The tall) boy (often) go (to the big) zoo.
(The hy) child --- went (his) home yesterday.
请分析下面句子的结构说出各个成分
1)I he two elder sisters. (我有两个姐姐。)
2) They don't swim very well.(他们游泳不太好。)
3) Do you go to school every day? (你每天去上学吗?)
4) I really want a cup of tea.(我真的想要一杯茶。)
5) Miss Smith teaches English very well.(史密斯先生教英语非常好。)
语法其实并没有一些人想象的那么可怕,其实里面有很多趣味。
第一讲 英语句子成分
WARM-UP:1)The teacher in the classroom. 2)Sang many songs and danced hily. 3)She attracts. 4)Many people living in the country. 5)All the books on the desk over there.
以上这些形式都不能构成英语句子。
英语句子(sentence)=主语+谓语(核心:主动词)
英语句子成分歌
英语句子八呀八大块, 主谓宾表真呀真实在;
补语跟着宾语表语跑, 定语同位(语)专把名词踹。
状语的位置它自由自在, 忽右忽左随心所欲摆。
浑身的毛病真呀真不少, 前后乱窜它还会加塞。(RAP)
I.八大成分的概念和构成
1.主语(名词代词形):句子的主体,是谓语陈述,说明的对象。
If you want the rainbow you he to put up with the rain.
不经历风雨,怎么见彩虹。
The secret of success is to start from scratch and keep on scratching.
成功的秘诀在于从磨练开始,并要坚持不断磨练。
充当主语的形式:1)名词2)代词3)名词短语4)名词从句5)数词6)不定式7)-ing形式8)介词短语(少见)
形式主语(名词从句,不定式,动名词)(见第六讲主语和宾语)
2.谓语:表示主语的行为或进行的活动。
I he a dream.
You don?t always want what you need, or need what you want.
所需之物未必皆所欲,所欲未必皆所需。
谓语形式:动词(英语句子的灵魂)
3.宾语:行为或活动的对象,接受者或受影响者。
You don?t find opportunities?you make them.
你找不到机会。你得去创造机会。
You probably won?t hear opportunity knock if your television is always on.
如果你常开着电视,你就可能听不到机会的敲门声。
充当宾语形式:1)名词2)代词3)名词短语4)名词从句5)数词6)不定式7)-ing形式
形式宾语(名词从句,不定式,动名词)(见第六讲主语和宾语)
4.表语:说明主语的身份和情况。(跟在系动词后)
Time is money.
Three o?clock is always too late or too early for anything you want to do.
你想做什么事,三点钟总是太早或太迟。
构成形式:1)名词2)形容词3)代词4)数词5)不定式6)ing形式7)过去分词8)副词9)介词短语10)小品词11)名词从句
5.补语:补充说明。(由动词类别来决定)
构成形式:1)名词2)代词3)形容词4)数词5)不定式6)-ing形式7)过去分词8)介词短语9)副词小品词10)名词从句
主语补语
Tom was made monitor.
宾语补语
I made Tom monitor.
表语补语
I am sure to succeed.
6. 定语:对名词性形式进行范围限定。
7. This is beautiful music.
There are only two kinds of music?good and bad.
自古音乐分两种,好的和坏的。
构成形式:1)限定词2)形容词3)名词4)数词5)不定式6)-ing形式7)过去分词8)介词短语9)副词10)关系从句
8. 同位语:对被修饰对象进行补充说明或进一步解释。
Puff, the magic dragon, lived by the sea.
构成形式:1)名词2)代词3)名词短语4)数词5)不定式6)-ing形式7)名词从句
9. 状语:修饰词,短语,从句和整句。位置:自由自在。
1)修饰性状语:修饰动词,形容词,副词等(时间,地点,肯定,否定,程度,频度,方式,伴随,原因,目的,比较等)。
Can you feel the love tonight?
Home never looks so good as when you come back from getting away from it.
只有出走又回家时,家才最感亲切。
2)连接性状语:连接上下文(顺序,递进,转折,让步,结果,推论,比较)。
First comes spring, then summer.
I?ve never been to America, therefore I don?t know much about it.
3)评述性状语:修饰整个句子,表示说话人的看法或态度。
Frankly speaking, the food is not very good.
II.成分关系
1.补语跟着宾语表语跑:
补语跟在宾语和表语的后面构成宾补和表补。把有宾补的句子变成被动语态,则宾补就变成了主补。
To love others makes us hy?to love ourselves makes us lonely.(宾补)
We are made hy to love others?we are made lonely to love ourselves.(主补)
爱他人使我们幸福,在自己使我们孤单。
2.定语,同位(语)专把名词踹:
定语,同位语修饰名词性形式
Experience is the best teacher.(被定语所修饰的形式为名词)
They are going to Melbourne, the beautiful city in southern Australia.(同位语所修饰的形式为名词)
3.谓语动词由状语修饰
When you reach for the stars, you may not quite get one, but you won?t come up with a handful of sand either.
你想摘下天上的星星,可能一个也摘不下;但也不会一无所获。
1、主语:
(1)由名词、代词(人称代词用主格)、动词不定式、动名词等充当,说明动作是?谁?发出的。如:The painter painted a very nice picture. (画家画了一幅漂亮的画。) / They fought against SARS brely. (他们勇敢地与非典搏斗。) / To see is to believe. (耳听为虚眼见为实). / Helping animals is to help people. (帮助动物就是帮助人类。)
(2)动词不定式或动名词做主语时可用it代替,而不定式或动名词移至表语或宾语之后。如:It is very comfortable to he a Class A seat during the long journey. (在长途旅行中能有个甲等座位简直太舒服了。) / Eating too much is bad for your health.(=It is bad for your health eating too much.) (吃得太多对你的身体不利。)
(3)口语中常见主语或?主--系?省略:(It is) nothing. ((那)没有什么。)/ (It) doesn?t matter. ((那)没有关系。) / (I) thank you. ((我)谢谢你。)
(4)反意问句的附加问句,主语必须是代词:The man looks worried,doesn?t he? (这个人看上去很着急不是吗?) / Tigers are dangerous animals, aren?t they? (老虎是危险的动物不是吗?)
(5)祈使句一般省略主语。加主语时往往用来指定某个人。Keep the keyboards clean, children. (孩子们请保持键盘的清洁。) (省略了主语) / You go there and fetch me a glass of water. (你去给我弄一杯水来。)
(6)主语一般在句首,但在问句中会处于第二位和句尾;倒装句及there be句型主语在动词之后。如:Computers are made in this factory. (计算机生产于这家工厂。) / Where are they? (他们在哪儿?) / Does the boy like staying home? (这个男孩喜欢呆在家里吗?)
(7)主语与谓语必须保持单、复数的一致, 而谓语与表语或宾语之间没有这一要求。Neither Jim nor Rose has passed the exam. (Jim和Rose都没有通过考试。) / The Chinese people are a hardworking and bre people. (中华民族是一个勤劳勇敢的民族。)
(8)主语可以由从句充当,详见?主语从句?。
2、谓语:
(1)由?不及物动词?、?及物动词+宾语?或?系动词+表语?等构成,说明主语所表示的人物?干什么?或?怎么样?。如:
He trelled in space for the first time.(他首次在太空旅行。) / Who teaches you English this year?(今年谁教你们的英语?) / The pizza has gone bad. (那块烤馅饼已经变坏。) /
(2)谓语动词必须反映出人称、单复数、时态等信息,谓语动词往往由下列词语依序排列构成:[情态动词]+[时态助动词]+[语态助动词]+[主要动词](不一定全部出现)。(见动词的时态和语态构成表) 记住:谓语部分第一个动词往往是变形动词。如:
I am sorry I am making so much noise but I he to. (对不起我发出了太大的声音但是只能这样。) / He can?t he finished reading the 800-page-long novel. (他不可能读完了那本长达800页的。) / Something must be done to stop the fowl flu from spreading out. (该取措施防止
禽流感蔓延。)
(3)谓语动词切忌用?行为动词1 + 原形动词?、?be + 原形动词?。
记住使用下列正确形式:
①情态动词+原形动词。如:You?d better go over the lesson.(你最好复习这一课。)
②shall/ will/ would+原形动词。如:They should he been there once.(他们应该去过那儿。)
③be+现在分词或者过去分词。如:What are you doing this evening?(今晚你打算做什么?)/ Many trees he been cut down since 10s.(自从20世纪70年代大批树木被砍伐。)
④he+过去分词。如:Many trees he been cut down since 10s.(意思同上)
⑤一般时问句和否定句中:do/does/did+原形动词。如:He does not enjoy himself very much.(他日子过的不好。)/ Did any of you see dinosaur eggs?(你们当中有谁见过恐龙蛋吗?)
⑥行为动词1+行为动词2 (不定式、动名词、现在分词、过去分词等形式)。如:He made up his mind to be a vet.(他拿定主意要做个兽医。)/ Feeling good about yourself is essential to feeling good about life.(自尊自爱是享受生活的根本。)/ They wake up the other family members, calling,?Merry Christmas!?(他们叫醒家庭的其他成员,呼喊着:圣诞快乐!)/ The kings of ancient Egypt had strong tombs built for themselves.(古代的埃及国王让人给他们自己修建坚固的坟墓。)
(4)不可用形容词、名词、代词、副词、介词短语等独立作谓语,必须在此之前加连系动词。
(5)谓语动词单复数形式:单数形式的动词有:is,was,has,does以及?动词+s?;复数形式的动词有:are,were,he以及动词原形。其他动词不分单、复数。
更多精彩内容请点击下一页
一、陈述句
用来陈述事实或观点的句子叫陈述句。朗读时用降调,句末用句号。陈述句分为肯定陈述句和否定陈述句两种形式。例如:
1. 肯定陈述句
(1) This is a desk.
(2) They look very young.
(3) You must look after your clothes.
(4) There is some money in the purse.
2. 否定陈述句
(1) They aren't my books.
(2) I don't know.
(3) Kate can't find her pen.
(4) There isn't a cat here. (= There's no cat here. )
二、祈使句
用来表示请求、命令、建议等的句子叫祈使句。祈使句的主语是you,常省略,谓语动词用原形。朗读时用降调,句末用句号。祈使句分为肯定祈使句和否定祈使句两种形式。例如:
1. 肯定祈使句
(1) Please go and ask the policeman.
(2) Come in, please.
2. 否定祈使句
(1) Don't worry.
(2) Don't be late for school.
三、疑问句
用来提问的句子叫疑问句。句末用问号,疑问句分为一般疑问句、选择疑问句和特殊疑问句等。
1. 一般疑问句
一般疑问句用来询问某事物和某情况是否属实,需要对方给予肯定 (yes) 或否定(no) 回答。朗读一般疑问句时用升调,句末用问号。例如:
(1) Is he a student?
(2) Can you spell it?
(3) Do you know?
(4) Are there any students in the classroom?
肯定回答 / 否定回答
(1) Yes, he is. / No, he isn't.
(2) Yes, I can. / No, I can't.
(3) Yes, we do. / No, we don't.
(4) Yes, there are. / No, there aren't.
2. 选择疑问句
从所提供的两个或两个以上选项中选择一个做出回答的疑问句叫选择疑问句。朗读时or前面的部分用升调,or后面的部分用降调,句末用问号。回答时要根据选项做出选择,不用yes或no来回答。例如:
—Is your friend a boy or a girl?
—He is a boy. / She is a girl.
3. 特殊疑问句
由what, who, whose, which, where, how等疑问词开头的疑问句叫特殊疑问句。朗读时用降调,句末用问号。回答时要做出具体回答,不用yes或no来回答。
特殊疑问句的语序分为两种:(1)陈述句语序。此时,疑问词作句子的主语或主语的修饰语。(2)疑问句语序。即:“疑问词 + 一般疑问句?”例如:
(1) —Who is on duty today?
—Li Lei is. (疑问词who作主语)
—Which bike is yours?
—The one under the tree. (疑问词which作bike的定语)
(2) —What else can you see in the picture?
—I can see some kites and a ball in it.
—How many books are there on the desk?
—Only one.
(一) 知识概要
初中所学的句型一般要分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。 陈述句中有肯定句与否定句之分。其中可以分为以下五种:
① 主语+不及物动词。如:I arrived at six last night.
② 主语+及物动词+宾语,如:I bought a good English Chinese Dictionary yesterday.
③ 主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语,如:Please tell me a story before I go to bed. 这样可加双宾语的句子有buy,tell, give, ask, pass, teach.
④ 主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语,如:I found it impossible to do it. Please keep the classroom clean and tidy.
⑤ 主语+系动词+表语,如:Tom is an American boy. The grass turned green in spring.在初中常见的句型中有There be…句型,表示存在某种事物,如:There is a map on the wall 其be动词的形式要与其后面相近的那个名词相一致。要注意的是这种句型加入助动词后,也要保持be动词,不要换用he,如:There is going to be a meeting tomorrow. 在句子结构中要注意主谓一致的问题,即句子的主语与谓语动词要相呼应。要注意的有如下几点:
① 用and连接两个主语时一般应视为复数,但如一人身兼两职时则要用单数谓语动词形式,如:A singer and dancer is coming to our party. a singer and dancer 既歌唱又可舞的演员。而 a singer and a dancer 则要译为:一位歌唱家和一位舞蹈家。②有些以 s 结尾的名词谓语动词要用单数,如: The news is good (news 为不可数名词)。
③ 有量词时应按量词的数量计算;如: This pair of glasses is good My glasses are broken.
④有些形单却意为复数的名词,如: People are coming here 这样的词还有 Police, 如果要讲一个警察时,应讲 a policeman。 两个警察为 two policemen。 又如 a policewoman, two policewomen
⑤ 所有不定代词 each, either, neither, one, the other, nobody, nothing, anyone, anything, someone, something … 要作为单数如: Someone is waiting for you 在并列句中表示联合关系的连词有: and not only … but also, neither … nor, either … or 如: My sister and my parents are going to the cinema。 表示转折关系的并列连词有: but 和 yet, 如: She is a good student, but she didn't pass the final exam. 又如: I think the news is strange, yet it is true 表示选择关系的连词有:or, either … or,如: Hurry up, or you will be late for school 表示因果关系的并列连词有: for, so 如: They studied very hard, so they all passed the exam
宾语从句
① 在及物动词的后面可以接一个名词来充当宾语,如: I knew the man, 而这时也可以用一个句子来充当宾语,如: I knew that he was a good man 这时宾语从句的连接词有 that, (that 只在从句中起联接作用,不在句中充当语法成分,既不是主语也不是宾语,所以在口语中常常被省略。如: I am sure (that) she has passed the exam
②if, whether 它们在宾语从句中只起连接作用,不起语法作用,当作是否讲。从句中有 or not 结构时,要用 whether, 如: I ask him if (whether) he has had his lunch I asks him whether he has had his lunch or not
③ what 它在宾语从句中除了作连接词外,还要作主语或宾语成份,如: I don't understand what you said (what 作 said 的宾语)。又如: I asked him what made him sick (what 在宾语从句中作主语)。
④ who,它也和what一样,在句中除作连接词外,可以充当句中的成份,如:I know who she is looking for?
⑤ whose 如: I want to know whose book this is?
⑥ which 如: Do you know which book is mine? 在连接词中还有4个常用的连接副词,① how 它的应用最广,如: how much, how many, how long, how soon, how old …。如: How much does it cost? ② when 它只是连接时间状语,如: Please tell me when the meeting will begin? ③ where 它连接地点状语,如: Where are you from? ④ why 它要连接的是原因状语从句,如: The teacher asked why Tom didn't come to school.
在考试中常见到的考点是: 宾语从句的时态与主句时态的呼应问题。
① 主句谓语动词如果是现在时或将来时,宾语从句的时态可以是任何所需要的时态, 如: I know he didn't come. 我知道他没来。 I know he will come tomorrow 我知道他明天来。I know he has gone to London 我知道他已去伦敦了。
②主句中的谓语动词若是过去时,宾语从句也要用过去时态中的某一种。比如: 一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时,过去完成时。除了在表达宇宙中的客观真理时,不能用现在时态。如: I wanted to know when he would come The teacher told me the earth moves around the sun
时间状语从句
其连接词有:after, before, when, as, as soon as, until (till), while, since, by 其中较难掌握的有以下几点:
① until (till) 直到,在用 until 表达时间状语的句子中,主句中的动词是要十分小心去选择。如动词是持续性动词,它要用肯定句,如: I studied hard until 12 o'clock last night. 如果动词是瞬间截止性动词,则要用否定句,如: He didn't go to bed until his mother came back
② 由 since, for, by, before 来引导的时间状语从句。 since 引导的时间状语是动作的开始时间,如: I he studied English since 1990. 而由 by 引导的时间状语通常是动作的结束时间,如: I had learned 25 English songs by the end of last term 而before 则多用于完成时, ago 则多用于一般过去时,如: He had finished his work before twelve yesterday I left my hometown two years ago
③ 在状语从句中用一般现在时或一般过去时表示将来。它们可能是主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时,如: If it rains, they won't go to the park on Sunday 也可以主句是一般过去时,从句用一般过去进行时,如: He said if it rained the next day he would not go to the park
考试中常见的考点有:要学生区别是条件、时间状语从句还是宾语从句,因在宾语从句中该用什么时态用什么时态,如: I want to know if he will come here tomorrow 在宾语从句中的条件状语从句与主句的关系,如: I want to know if it rains he will come here tomorrow
原因状语
① because, 应译为"因为"。它表达的因果关系最强,如: He didn't pass the exam because he didn't study hard
② since 应译为"既然",如: Since you were ill yesterday I left some notes on your desk
③ as 应译为"由于",如: As it is too hot we'd better go swimming since 与 as 所表达的因果关系远比 because 弱得多。而 for 表达的因果关系最弱。它不能用于句首,如: He studies hard, for he wants to go to college
比较状语从句
同级比较 as … as, 如: This book is as good as that one 要注意的有两点:
① as … as 中间要用原级而不是比较级。
② 用形容词还是副词,如: Mary writes as carefully as Tom 而其否定句为 not as (so) … as, 如: They didn't work so hard as we did, 而不同级比较用比较级加 than, 如: He is younger than I am
要注意的是表示"越来越"这一概念时有两个句型:
① 比较级+and+比较级,如: The days are getting longer and longer The little girl is becoming more and more beautiful
② 定冠词 the + 比较级+ the + 比较级,如: The harder you study, the more you can learn 方式状语中要注意的是as (连词)与 like (介词)的区别。 as 作为连词其后接从句,如: Please do it as I did it 但后面的句子常作省略,如: Please do it as I 而 like 是介词,其后要接的是宾语,如: Please do it like me
结果和目的状语从句
主要有 so … that, so that, in order that等几种用法。
① so … that 用在单数可数名词前,so + 形容词 + a + 名词 + that,如: She is so beautiful a girl that everyone likes her 或用 such + a + 形容词 + 名词 + that, 如: She is such a beautiful girl that everyone likes her
② 在不可数名词或可数名词复数前只能用 such, 如: It is such good weather we want to go for a picnic 又如: They are such good players that they should win the game.
③ 在much, many, few, little 之前只能用so, 如: I he so little money that I can't buy it
④ so … that 之间只有形容词时,则不能用 such, 如: It is so good that I want to buy
⑤ so that 其后接从句,如: I got up earlier so that I could catch the first bus
声明:本站所有文章资源内容,如无特殊说明或标注,均为采集网络资源。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。